Discuss the “Lee model” for point to point propagation
6. Discuss the “Lee model” for point to point propagation.
In general, the mobile point-to-point model can be obtain in three steps.
(i) Generate a standard condition.
(ii) Obtain an Area-to-Area prediction model.
(iii) Obtain a mobile Point-to-Point model using Area-to-Area prediction model.
The purpose of developing this model is try to separate two effects.
(a) Natural terrain contour.
(b) Human made structures.
(i) Standard Condition: To generate the standard condition, transmitted power and antenna height at base station and mobile unit should satisfy the following requirements.
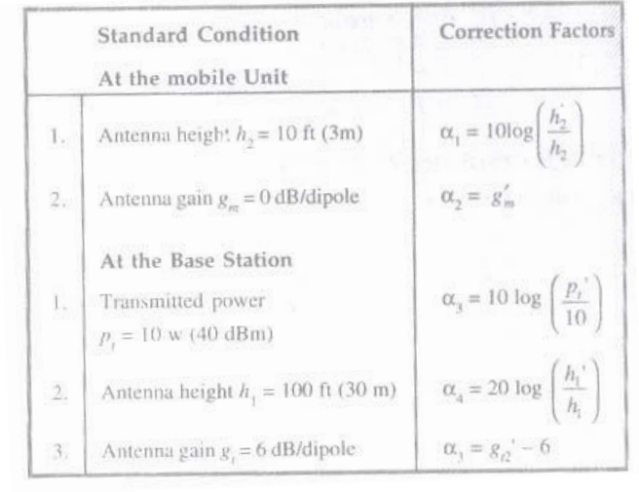 |
| standard condition |
(ii) Obtain Area-to-Area Predication Curves for Human Made Structures: In the Area-to-Area prediction model, all the areas are considered. as flat even though the data may be received from non flat area
(iii) Effect of the Human Made Structures: The terrain configuration of each city is different, and the human made structure of the each city unique. So that, try to separate the two effects. The path loss curve obtained on virtually flat ground indicates the effects of the signal loss due to solely human made structures. The average path loss slope shown below which is a combination of measurements from high spots and low spots along different radio paths.
The Area-to-A prediction curve is obtained from the mean value of the measured data and used for further prediction in that area The Area-to-Area prediction model can be used as a first step towards achieving the point-to-point prediction model. The performance of d Area-to-Area prediction model can be represented by two parameters.
1. 1 mi intercept point.
2. The path loss slope.
The 1 ml intercept point is the power received at a distance of 1 mi from the transmitter. The 1 mi intercept point is depends upon the effective antenna height gain.
ΔG = Effective antenna – height gain = 20 log(he/h1)
Where, he= Effective antenna height
h1= Actual height


