Explain the phenomena of severe fading?
3. Explain the phenomena of severe fading?
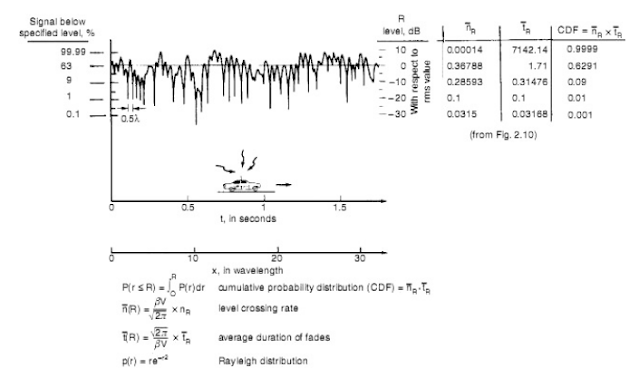
Severe Fading:
If the antenna height of the mobile unit is lower than its typical surroundings, and the carrier frequency wavelength is much less than the sizes of the surrounding structures, multi path waves are generated. At the mobile unit, the sum of the multi path waves causes a signal-fading phenomenon. The signal fluctuates in a range of about 40 dB (10 dB above and 30 dB below the average signal). We can visualise the nulls of the fluctuation at the base band at about every half wavelength in space, but all nulls do not occur at the same level, as Fig.3 shows. If the mobile unit moves fast, the rate of fluctuation is fast. For instance, at 850 MHz, the wavelength is roughly 0.35 m (1 ft). If the speed of the mobile unit is 24 km/h (15 mi/h), or 6.7 m/s, the rate of fluctuation of the signal reception at a 10-dB level below the average power of a fading signal is 15 nulls per second.
 |
| A typical fading signal received while the mobile unit is moving |

