Derive the noise margins for a CMOS inverter
March 05, 2024
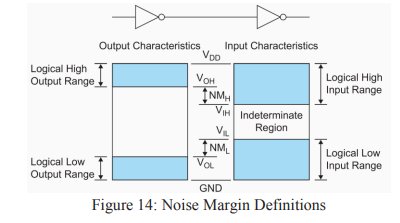
(iii) Noise Margins:
- Noise margin (Noise immunity) is related to the DC voltage characteristics.
- Noise Margin allows determining the allowable noise voltage on the input of a gate, so that the output will not be corrupted.
- Two parameters of the noise margin are LOW noise margin (NML), and the HIGH noise margin (NMH).
- NML is defined as the difference in maximum LOW input voltage VIL and the maximum LOW output voltage VOL. NML = VIL - VOL
- The value of NMH is the difference between the minimum HIGH output voltage VOH and the minimum HIGH input voltage VIH. i.e., NMH = VOH - VIH
- Inputs between VIL and VIH are said to be in the indeterminate region or forbidden zone.
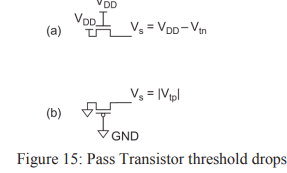
(iv) Pass Transistor DC Characteristics:
- The nMOS transistors pass 0’s well but 1’s poorly. Figure 15(a), shows an nMOS transistor with the gate and drain tied to VDD.
- Initially at Vs = 0. Vgs > Vtn, so the transistor is ON and current flow.
- Therefore, nMOS transistors attempting to pass a 1 never pull the source above VDD – Vtn. This loss is called a threshold drop.
- The pMOS transistors pass 1’s well but 0’s poorly.
- If the pMOS source drops below |Vtp|, the transistor cuts off.
- Hence, pMOS transistors only pull down to a threshold above GND, as shown in Figure 15(b).