What are the different types of noises in cellular frequency ranges Explain in detail?
8. What are the different types of noises in cellular frequency ranges Explain in detail?
Noise level in cellular frequency band: The thermal noise kTB at a temperature T of 290 K (17°C) and a bandwidth B of 30 kHz is -129 dBm, where k is Boltzmann’s constant. Assume that the received front end noise is 9 dB, and then the noise level is -120 dBm.
There are two kinds of man-made noise, the ignition noise generated by the vehicles and the noise generated by 800-MHz emissions.
The ignition noise: In the past, 800 MHz was not widely used. Therefore, the man-made noise at 800 MHz is merely generated by the vehicle ignition noise. The automotive noise introduced at 800 MHz with a bandwidth of 30 kHz can be deduced from Fig.7.
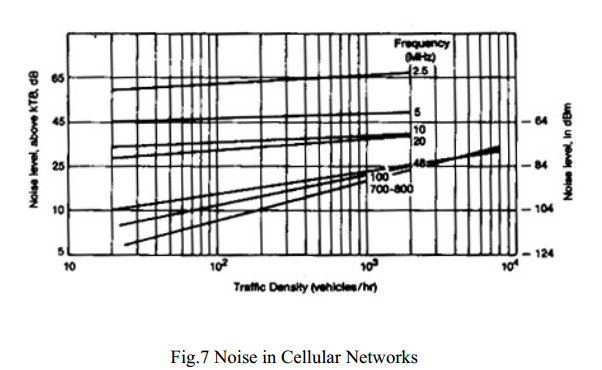 |
| Noise in Cellular Networks |
The 800-MHz emission noise: As a result of the cellular mobile systems operating in all the major cities in the United States and the spurious energy generated outside each channel bandwidth, the early noise data measurements are no longer valid. The 800-MHz-emission noise can be measured at an idle channel (a forward voice channel) in the 869- to 894-MHz region while the mobile receiver is operating on a car battery in a no-traffic spot in a city. In this Case, no automotive ignition noise is involved and no channe1 operation is in the proximity of the idle-channel receiver. We found that in some areas the noise level is 2 to 3 dB higher than -120 dBm at the cell sites and 3 to 4 dB higher than -120 dBm at the mobile stations.
Amplifier noise: A mobile radio signal received by a receiving antenna, either at the cell site or at the mobile unit, will be amplified by an amplifier. We would like to understand bow the signal is affected by the amplifier noise. Assume that the amplifier baa an available power gain g and the available noise power at the output is N. The input signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio is Ps/Ni, the output signal-to-noise ratio is Po/No, and the internal amplifier noise is Na. Then the output Po/No becomes
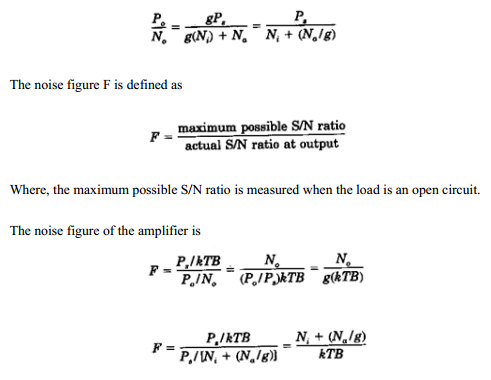 |
| Amplifier noise |
The term kTB is the thermal noise. The noise figure is a reference measurement between a minimum noise level due to thermal noise and the noise level generated by both the external and internal noise of an amplifier.

