Discuss the merits of point-to-point model
4. Discuss the merits of point-to-point model.
The area-to-area model usually only provides an accuracy of prediction with a standard deviation of 8 dB, which means that 68 percent of the actual path-loss data are within the ± 8 dB of the predicted value. The uncertainty range is too large. The point-to-point model reduces the uncertainty range by including the detailed terrain contour information in the path-loss predictions.
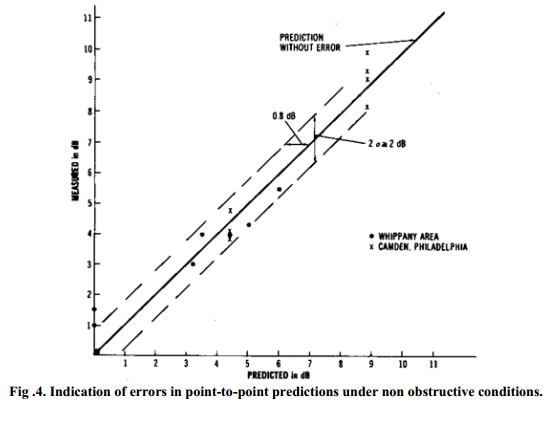
The differences between the predicted values and the measured ones for the point-to-point model were determined in many areas. In the following discussion, we compare the differences shown in the Whippany, N.J., area and the Camden-Philadelphia area. First, we plot the points with predicted values at the x-axis and the measured values at the y-axis, shown in Fig. 4. The 450 line is the line of prediction
without error. The dots are data from the Whippany area, and the crosses are data from the Camden Philadelphia area. Most of them, except the one at 9 dB, are close to the line of prediction without error.
The mean value of all the data is right on the line of prediction without error. The standard deviation of the predicted value of 0.8 dB from the measured one.
In other areas, the differences were slightly larger. However, the standard deviation of the predicted value never exceeds the measured one by more than 3 dB. The standard deviation range is much reduced as compared with the maximum of 8 dB from area-to-area models. The point-to-point model is very useful for designing a mobile cellular system with a radius for each cell of 10 mi or less. Because the data
follow the log-normal distribution, 68 percent of predicted values obtained from a point-to-point prediction model are within 2 to 3 dB. This point-to-point prediction can be used to provide overall coverage of all cell sites and to avoid cochannel interference. Moreover, the occurrence of handoff in the cellular system can be predicted more accurately.
The point-to-point prediction model is a basic tool that is used to generate a signal coverage map, an interference area map, a hand off occurrence map, or an optimum system design configuration, to name a few applications.