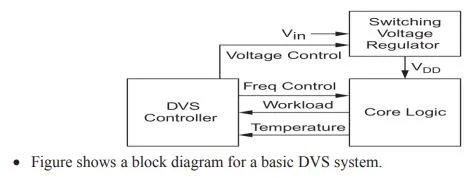
Describe how dynamic voltage scaling can reduce dynamic power dissipation
March 14, 2024
Dynamic voltage scaling (DVS):
- Systems can save large amounts of energy by reducing the clock frequency, then reducing the supply voltage.
- This is called dynamic voltage scaling (DVS) or dynamic voltage/frequency scaling (DVFS).
- It determines the supply voltage and clock frequency sufficient to complete the workload on schedule or to maximize performance without overheating.
Frequency:
- Dynamic power is directly proportional to frequency, so a chip should not run faster than necessary.
- Reducing the frequency allows downsizing transistors or using a lower supply voltage.
Low Power Architecture
- Device Level
- Low Capacitance in device and Multi Threshold Devices
- DVFS – Dynamic Voltage Frequency Scaling
- Multi VDD
- Gate Sizing
- Voltage Islands
- Power Gating
- Clock Gating
- Parallelism and Pipelined micro-architecture
Parallel Computations
• Multiple cores
• Multiple Issue pipelines
• Linear power increase
Pipelining
• Faster clock
• Exponential power increase
• Longer branch miss-predictions