INTRODUCTION TO VLSI
- In 1958, Jack Kilby built the first integrated circuit flip-flop at Texas Instruments.
- Bell Labs developed the bipolar junction transistor. Bipolar transistors were more reliable, less noisy and more power-efficient.
- In 1960s, Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) began to enter in the production.
- MOSFETs offer the compelling advantage that; they draw almost zero control current while idle.
- They come in two flavors: nMOS and pMOS, using n-type and p-type silicon respectively.
- In 1963, Frank Wanlass at Fairchild described the first logic gates using MOSFETs.
- Fairchild’s gates used both nMOS and pMOS transistors, naming as Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS).
- Power consumption became a major issue in the 1980s as hundreds of thousands of transistors were integrated onto a single die.
- CMOS processes were widely adopted and replaced nMOS and bipolar processes for all digital logic applications.
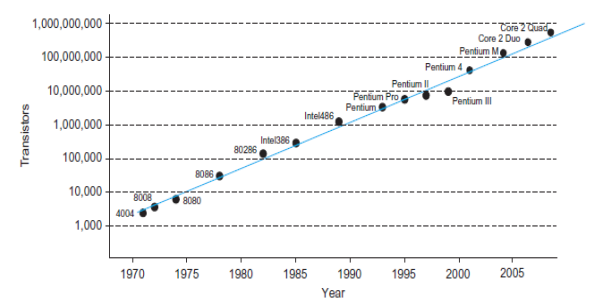
- In 1965, Gordon Moore observed that plotting the number of transistors that can be most economically manufactured on a chip gives a straight line on a semi logarithmic scale.
o Moore’s Law is defined as transistor count doubling every 18 months.
The level of integration of chips is classified as
- Small Scale Integration (SSI)
- Medium Scale Integration (MSI)
- Large Scale Integration (LSI)
- Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI)
- Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI)
1. Small scale Integration:
Small-Scale Integration (SSI) circuits have less than 10 gates. Example: 7404 inverter.
2. Medium scale Integration:
Medium-Scale Integration (MSI) circuits have up to 1000 gates. Example: 74161 counter.
3. Large scale Integration:
Large-Scale Integration (LSI) circuits have up to 10,000 gates. Example: 8-bit microprocessor (8085).
4. Very large scale Integration:
Very large scale Integration (VLSI) with gates counting up to lakhs. Example: 16-bit microprocessor (8086).
The feature size of a CMOS manufacturing process refers to the minimum dimension of a transistor that can be reliably built.
5. Ultra large scale Integration:
Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) is the process of integrating millions of transistors on a single silicon semiconductor microchip.