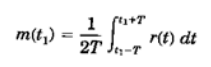Explain about the model of transmission medium
14. Explain about the model of transmission medium.
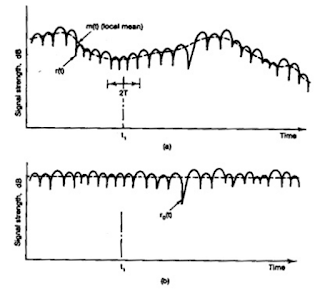
Model of transmission medium: A mobile radio signal r(t), illustrated in Fig.14, can be artificially characterised by two components m(t) and r(t) based on natural physical phenomena.
r(t) = m(t) ro(t)
The component m(t) is called local mean, long-term fading, or log normal fading and its variation is due to the terrain contour between the base station and the mobile unit. The factor r0 is called multi path fading, short term fading, or Rayleigh fading and its variation is due to the waves reflected from the surrounding buildings and other structures. The long-term fading m(t) can be obtained from Eq. below
Where 2T is the time interval for averaging r(t). T can be determined based on the fading rate of r(t), usually 40 to 80 fades. Therefore, m(t) is the envelope of r(t), as shown in Fig.10. Equation also can be expressed in spatial scale as
The length of 2L has been determined to be 20 to 40 wavelengths. Using 36 or up to 50 samples in an interval of 40 wavelengths is an adequate averaging process for obtaining the local means.
The factor m(t) or m(x) is also found to be a lognormal distribution based on its characteristics caused by the terrain contour. The short- term fading r0 is obtained by
The factor ro(t) follows a Rayleigh distribution, assuming that only reflected waves from local surroundings are the ones received (a normal situation for the mobile radio environment). Therefore, the term Rayleigh fading is often used.
 |
| mobile radio signal fading representation |