Differential Cascode voltage switch with pass gate logic (DCVSPG)
March 12, 2024
- Explain about DCVSL logic with suitable example.
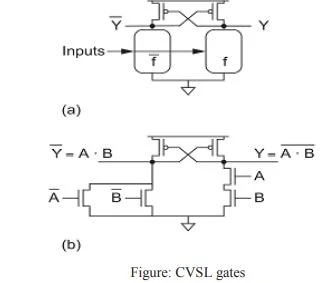
- Cascode Voltage Switch Logic (CVSL) seeks the benefits of ratioed circuits without the static power consumption.
- It uses both true and complementary input signals and computes both true and complementary outputs using a pair of nMOS pulldown networks, as shown in Figure (a).
- The pulldown network f implements the logic function as in a static CMOS gate, while
- fuses inverted inputs feeding transistors arranged in the conduction complement.
- For any given input pattern, one of the pulldown networks will be ON and the other OFF.
- The pulldown network that is ON will pull that output low.
- This low output turns ON the pMOS transistor to pull the opposite output high.
- When the opposite output rises, the other pMOS transistor turns OFF, so no static power dissipation occurs.
- Figure (b) shows a CVSL AND/NAND gate.
Advantage:
CVSL has a potential speed advantage because all of the logic is performed with nMOS transistors, thus reducing the input capacitance.
 |
| CVSL gates |

