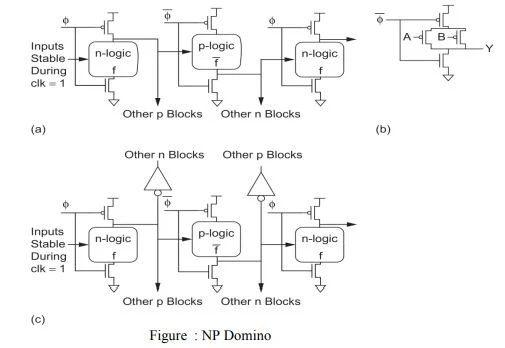
NP and Zipper Domino
March 13, 2024
- Describe the basic principle of operation of NP domino logic.
- The HI-skew inverting static gates are replaced with predischarged dynamic gates using pMOS logic.
- A footed dynamic p-logic NAND gate is shown in Figure (b). When ф is 0, the first and third stages precharge high while the second stage predischarges low.
- When ф rises, all the stages evaluate. Domino connections are possible, as shown in Figure (c).
- The design style is called NP Domino or NORA Domino (NO RAce).
NORA has two major drawbacks.
(i) The logical effort of footed p-logic gates is worse than that of HI-skew gates.
(ii) NORA is extremely susceptible to noise.
- In an ordinary dynamic gate, the input has a low noise margin (about Vt ), but is strongly driven by a static CMOS gate.
- The floating dynamic output is more prone to noise from coupling and charge sharing, but drives another static CMOS gate with a larger noise margin.
- In NORA, however, the sensitive dynamic inputs are driven by noise prone dynamic outputs.
- Besides drawback and the extra clock phase requirement, there is little reason to use NORA.
- Zipper domino is a closely related technique, that leaves the precharge transistors slightly ON during evaluation by using precharge clocks. This swing between 0 and VDD – |Vtp| for the pMOS precharge and Vtn and VDD for the nMOS precharge.